

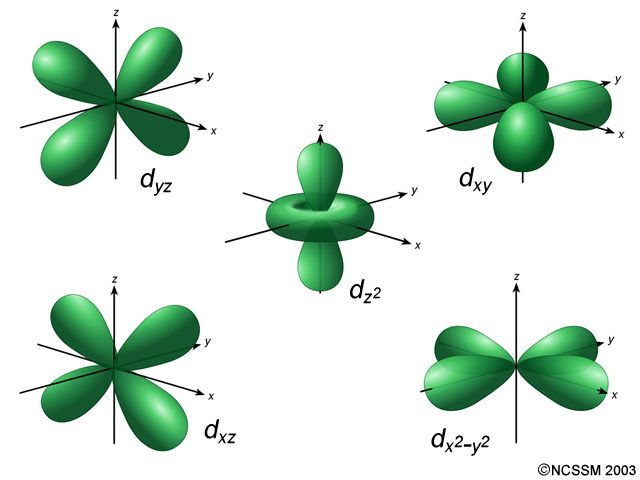
The most probable region of electron rotation around the nucleus is called the orbital. These sub-energy levels are also called orbital. Electron configuration of platinum through orbitalĪtomic energy shells are subdivided into sub-energy levels. The electron configuration of all the elements can be done through the orbital diagram. The electron configuration of an element with an atomic number greater than 18 cannot be properly determined according to the Bohr atomic model. Electrons can be arranged correctly through orbits from elements 1 to 18. Therefore, the order of the number of electrons in each shell of the platinum(Pt) atom is 2, 8, 18, 32, 17, 1. Therefore, a platinum atom will have two electrons in the first shell, eight in the 2nd orbit, eighteen electrons in the 3rd shell, and thirty-two in the 4th shell.Īccording to Bohr’s formula, the fifth shell will have eighteen electrons but the fifth shell of platinum will have seventeen electrons and the remaining one electron will be in the sixth shell. That is, the number of electrons in platinum is seventy-eight. The atomic number is the number of electrons in that element. Platinum atom electron configuration (Bohr model) Therefore, the maximum electron holding capacity in the first shell is two, the second shell is eight and the 3rd shell can have a maximum of eighteen electrons. The maximum electrons holding capacity in N orbit is 2n 2 = 2 × 4 2 = 32. The maximum electrons holding capacity in M orbit is 2n 2 = 2 × 3 2 = 18. The maximum electron holding capacity in L orbit is 2n 2 = 2 × 2 2 = 8. The maximum electron holding capacity in K orbit is 2n 2 = 2 × 1 2 = 2. The electron holding capacity of each orbit is 2n 2. K is the name of the first orbit, L is the second, M is the third, and N is the name of the fourth orbit. These circular paths are called orbit(shell). The electrons of the atom revolve around the nucleus in a certain circular path. The complete idea of the orbit is given there. Scientist Niels Bohr was the first to give an idea of the atom’s orbit. Platinum atom electron configuration through orbit For example Aufbau principle, Hund’s principle, and Pauli’s exclusion principle. Electron configuration through orbital (Aufbau principle)Įlectron configuration through orbitals follows different principles.Electron configuration through orbit (Bohr principle).Electron configuration can be done in two ways. The electron configuration of platinum is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 3d 10 4s 2 4p 6 4d 10 4f 14 5s 2 5p 6 5d 9 6s 1, if the electron arrangement is through orbitals. The arrangement of electrons in platinum in specific rules in different orbits and orbitals is called the electron configuration of platinum. These electrons are arranged according to specific rules in different orbitals. The total number of electrons in platinum is seventy-eight.

What is the electron configuration of platinum? Hopefully, after reading this article, you will know more about this topic.
4d orbital how to#
I also discussed how to draw and write an orbital diagram of platinum. In this article, I have discussed in detail how to easily write the complete electron configuration of platinum. Platinum is a classified transition metal element. Electron configurations, filling orbitals, and valence electrons of 4d elements Atomic Numberġs 2 2s 2p 6 3s 2p 6d 10 4s 2p 6d 10 5s 1ġs 2 2s 2p 6 3s 2p 6d 10 4s 2p 6d 10 5s 2įigure 4696 shows the relation between electron binding energies and atomic number (Z).Platinum is the 78th element in the periodic table and its symbol is ‘Pt’. Table 4696a shows the 4d elements in periodic table. This book (Practical Electron Microscopy and Database) is a reference for TEM and SEM students, operators, engineers, technicians, managers, and researchers.ĮELS data on the occupancies of 3d and 4d states can clarify many fundamental problems related to the electronic properties of transition metal alloys.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
